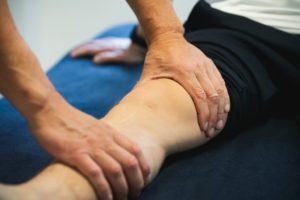
What is fluid in the knee?
Fluid in the knee occurs when extra joint fluid builds up in or around the knee joint. This can be the result of an injury, overuse, inflammation or an underlying condition such as osteoarthritis or rheumatism. The knee swells and often feels warm and tight. Bending or straightening the leg can be painful or limited.
Possible causes
There are several causes that can lead to fluid accumulation in the knee:
Trauma or injury: For example, a sprain, meniscus tear or cruciate ligament injury.
Overload: Too much repetitive movement or exercising without adequate recovery.
Inflammations: Such as arthritis or gout.
Arthrosis: Wear and tear of the cartilage causes irritation and fluid production.
Infection: Less common, but serious and requires medical treatment.
Symptoms of fluid in the knee
Recognizable symptoms include:
Swelling of the knee
Tight skin around the joint
Pain when moving or straining
Limited freedom of movement
Feeling of instability
If you recognize these complaints, it is wise to make an appointment with your GP or physiotherapist.
Treatment of fluid in the knee
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. In most cases, the following steps are effective:
1. Rest and relieve
Avoid overloading the knee joint. Try to limit activities such as climbing stairs or standing for long periods. Sometimes it is advised to walk with crutches temporarily.
2. Cooling
A cold pack helps to reduce swelling. Place it on the knee for 10-15 minutes, several times a day.
3. Compression and hold high
A pressure bandage can help to reduce swelling. Also keep the knee elevated regularly, for example on a pillow.
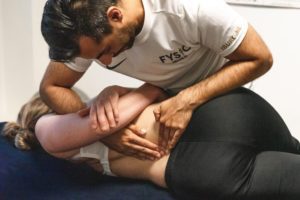
4. Physiotherapy
A physiotherapist will create a personal treatment plan, aimed at improving stability, muscle strength and mobility of the knee. Sometimes exercise therapy is combined with manual therapy or medical taping.
5. Medication
In case of inflammation, a doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medication. In some cases, fluid is drained or an injection of corticosteroids is given.
What can you do yourself?
In addition to professional help, you can contribute to your recovery yourself:
Maintain a healthy weight to avoid extra pressure on the knee
Do gentle exercises regularly to stimulate blood circulation
Wear supportive shoes
Avoid prolonged periods of kneeling or squatting
When to see a physiotherapist?
If the swelling persists or returns, guidance by a physiotherapist is recommended. We at Fysiotherapie Iburg in Rotterdam are happy to help you with a targeted approach to tackle the cause and prevent recurrence.
Would you like personal advice about fluid in the knee? Contact us today for an intake interview.